The #1 platform for secure data exchange.
The best choice for exchanging sensitive files securely and in compliance with the law. Made & hosted in Germany.












Your solution for comprehensive secure data exchange. Gain full control over the exchange of your sensitive business data with FTAPI.
100% compliant & worry-free
80% time savings for your IT
2,000+ satisfied customers
100% control & transparency
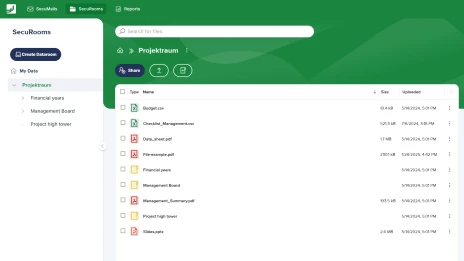
The platform. Even complex data exchange challenges can be solved securely and efficiently thanks to four combinable products.
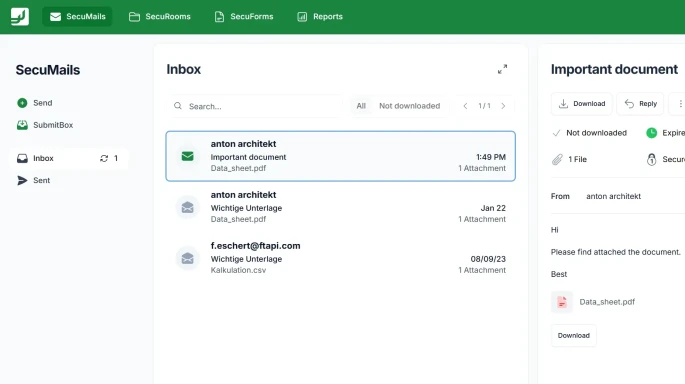
Secure emails made easy
Send and receive files of any size while adhering to compliance requirements. Whether via Outlook or in the browser, without complicated key exchange, simply with a few clicks.
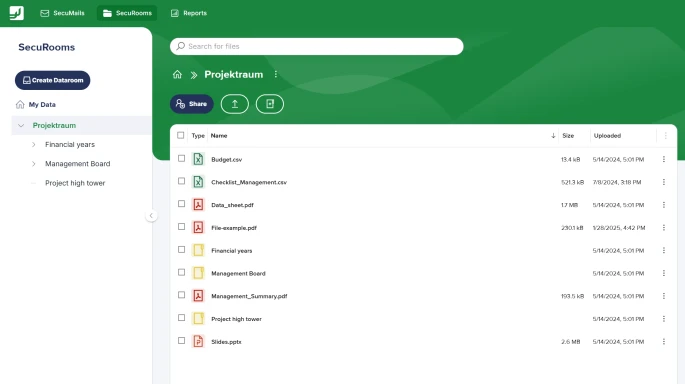
Store, share and collaboratively use data
Upload sensitive files easily via drag & drop and share sensitive content securely online with internal and external people. Immediately ready for use in the browser and can be used directly without extensive IT knowledge.
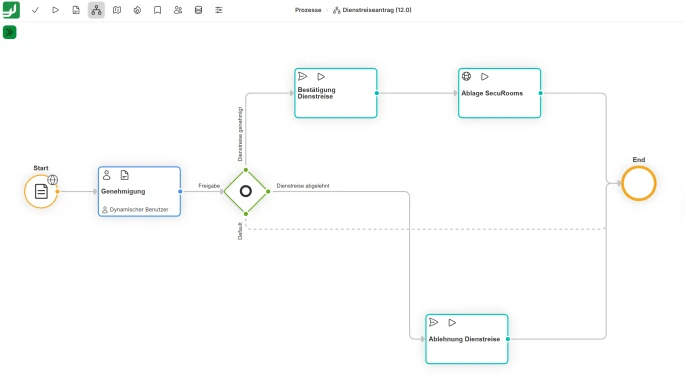
Automate business processes
Say goodbye to repetitive, error-prone workflows and automate data processes, e.g. for your HR department or accounting.
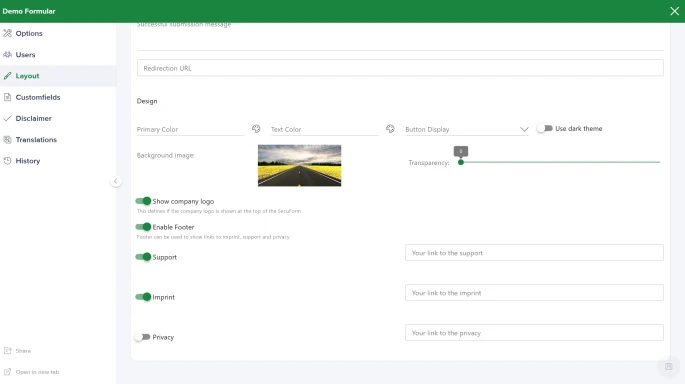
Structured data input
Create your own forms, perfectly customised to your needs. This creates the basis for fast and efficient further processing of data.
Our integrations. FTAPI connects to the most common applications without additional programming or major configuration effort.









Register for news, tips and more.
Immerse yourself in a world of knowledge and inspiration with exclusive white papers, engaging expert interviews, and personal invitations to events that truly help you grow and connect with the industry.









